Smart Specialization is a European innovation policy characterized by the identification and strengthening of regional competitive advantages with wide stakeholder involvement. In the context of the European Green Deal and the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, Smart Specialization Strategies are facing a transition towards Smart Sustainable Specialization Strategies - strategies in which sustainability is a core factor. ARIES4 is an alliance of four European regions pioneering such transition. It aims to create a scheme of cooperation and flow of knowledge among the main actors of smart specialization strategies: universities, vocational training providers, the public sector, the business sector, and the broader society.
LATEST NEWS

Presentation of the results of the ARIES4 project in Navarre
Pamplona, June 17, 2025. ARIES4 project coordinator Martin Larraza and work package 2 leader Nuria Osés participated in the conference on Circular Economy Indicators in Navarra. This conference was held within the framework of the Navarre...
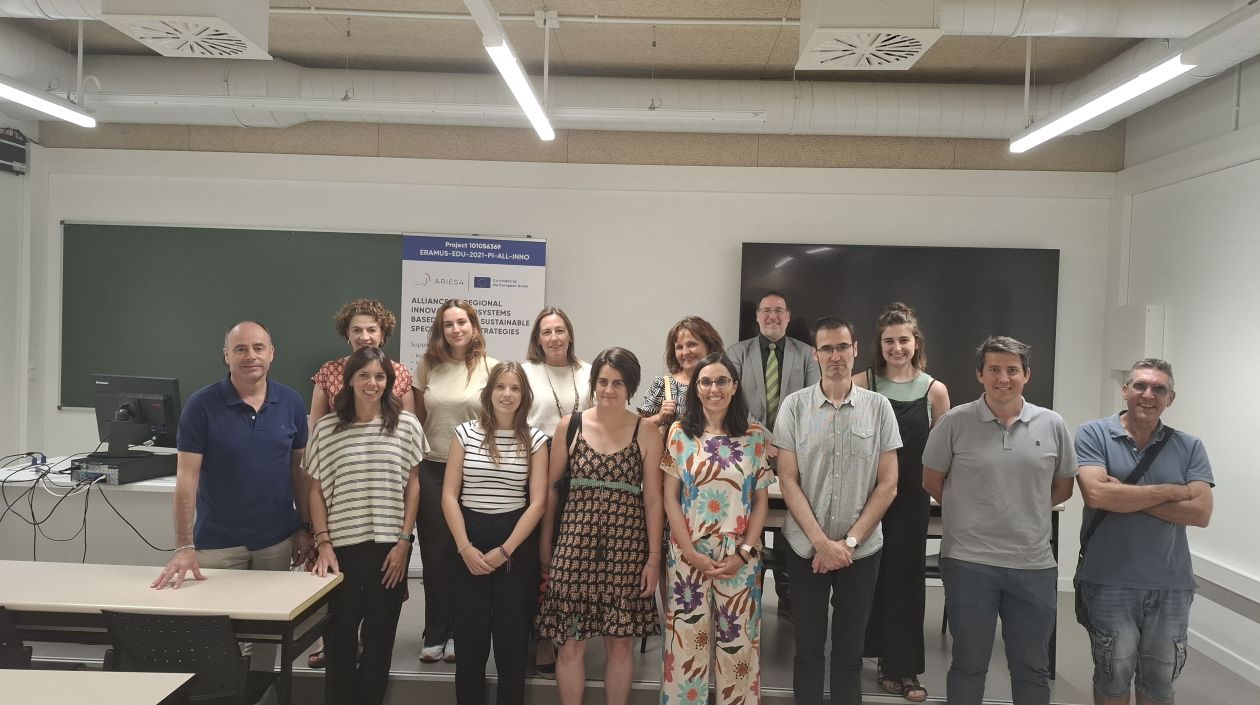

The challenges of the circular economy: cases and indicators in the context of the ARIES4 project
Pamplona, 25 June 2025 - Coinciding with the last class of the course Business leadership in circular economy: innovation and sustainability, one of the two training programmes funded by the ARIES4 project, a special session was held to present the...

Regional Workshop in Värmland: How Sustainability Can Drive Smart Specialisation
The second regional workshop within the ARIES4 project in Värmland was recently held – this time focusing on businesses and clusters working with sustainable business development and innovation. The aim was to demonstrate how sustainability can...
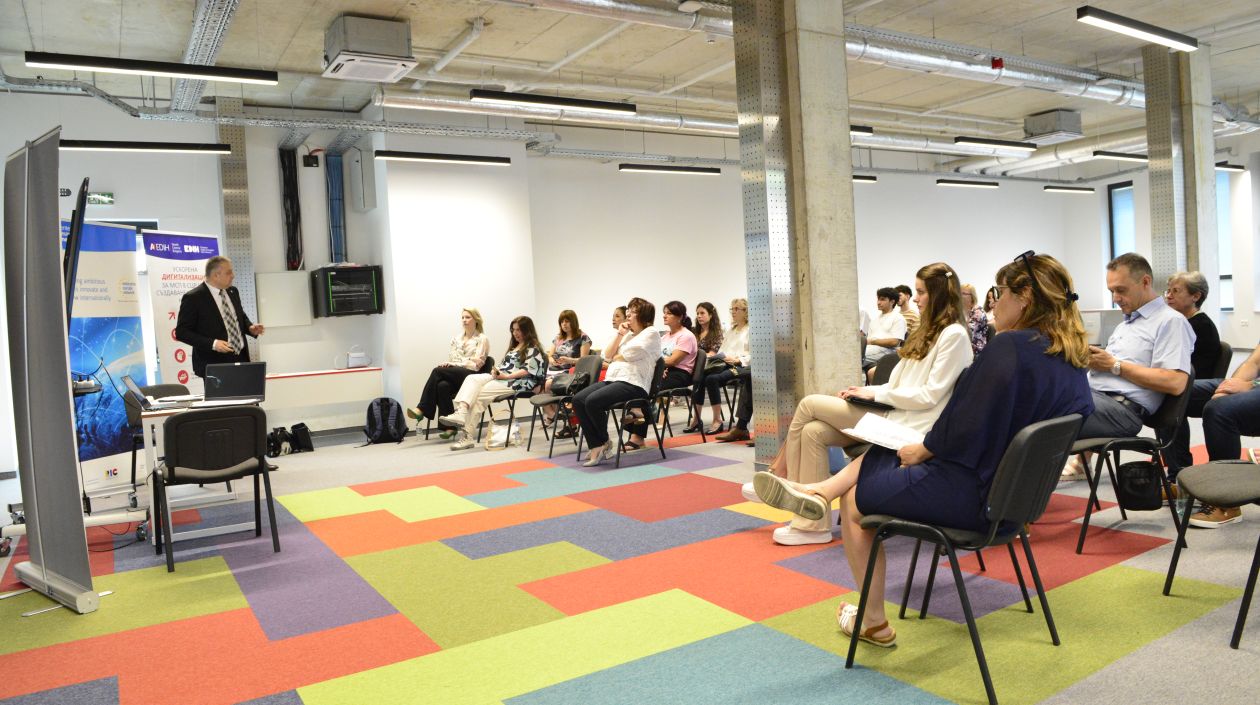

Business Forum: Sustainability, Innovation & International Cooperation
Gabrovo | 12 June 2025 Thirty-two representatives from the business community, local and regional authorities, and educational institutions gathered in Gabrovo to take part in the Business Forum “Sustainability, Innovation and...
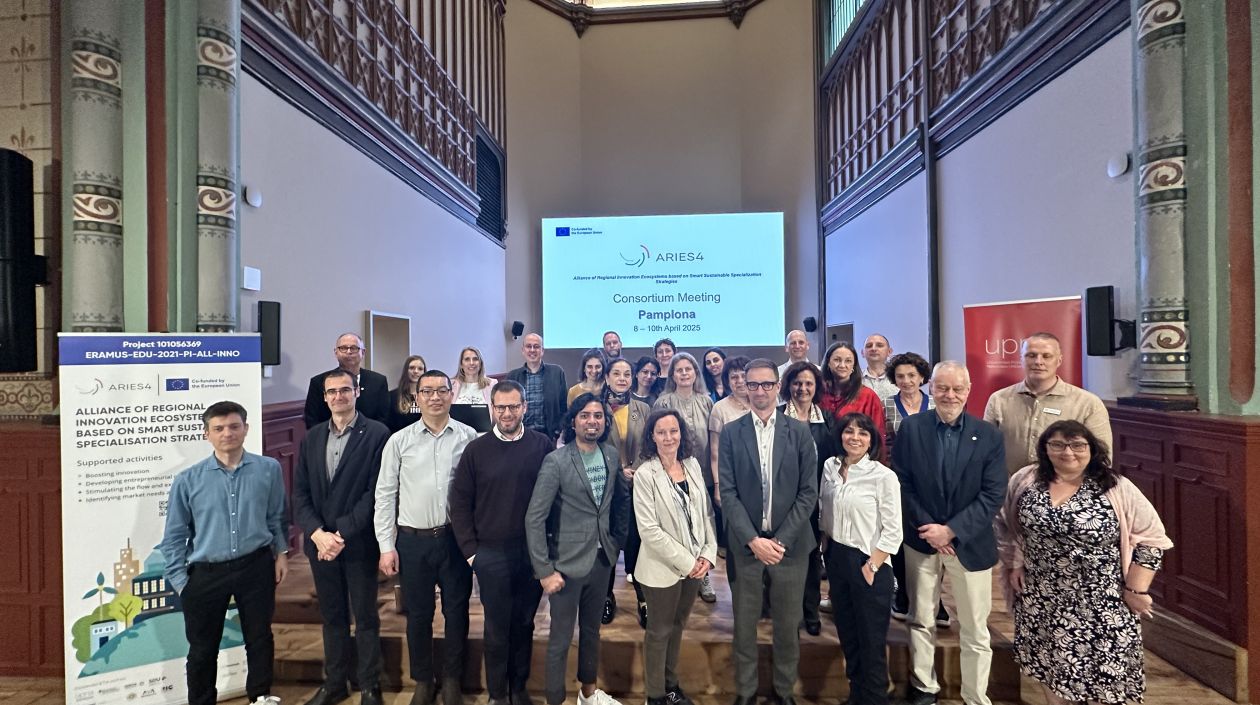

Pamplona hosts the last meeting of the ARIES4 project
Pamplona hosted the closing meeting of the European project ARIES4. This initiative has brought together for three years the regions of Navarra (Spain), Värmland (Sweden), South Denmark (Denmark) and Gabrovo (Bulgaria) with the aim of strengthening...
More Articles
- Researchers and Food Producers Discuss How to Increase the Perceived Value of Local FoodMonday, 07 April 2025 14:08
- Swedish Students' Tips: Turning Resistance into Pride in the Energy TransitionTuesday, 25 February 2025 17:42
- UPNA and VET students work together to solve a sustainability challenge proposed by AN GroupThursday, 13 February 2025 10:20
- Debate On Sustainability In The Agri-Food Sector in Tudela (Navarre)Friday, 07 February 2025 09:31
- International workshop for S3 managers, institutions, policy makers and companies involved in the...Monday, 03 February 2025 06:39
- Sustainability Challenges in the IT sector in Gabrovo, BGSunday, 01 December 2024 18:25
- Students Present Sustainability Ideas at ARIES 4 CRE8 Case CompetitionSunday, 01 December 2024 15:30
- Game Plan for Monitoring Sustainability Presented to Strategists and StudentsFriday, 15 November 2024 11:04
- Katrin Simon Presents ARIES4 Project at Foodnauta EventWednesday, 16 October 2024 19:31
- Energy Companies Discussed Status and Needs in Sustainability WorkThursday, 16 May 2024 08:38
- Presentation at the Master's Degree in Agricultural Engineering UPNA on the MOA FoodTech case study: Green...Thursday, 09 May 2024 18:41
- Manufacturing industry in Gabrovo debate on sustainability challengesMonday, 29 April 2024 10:25
- Gabrovo youth support business sustainability through creative solutionsMonday, 29 April 2024 08:42
- Case Presentation "Be Planet, Sustainability as a Business at BeePlanet" in the Master's Program in...Monday, 22 April 2024 12:16
- Renewable Energy Sector Debate in SpainMonday, 22 April 2024 08:10
- Driving Change Together: ARIES4 Case Symposium Sparks Sustainable Solutions for SMEsMonday, 19 February 2024 12:16
- CRE8® event in PamplonaWednesday, 14 February 2024 16:44
- Case Presentation of Moa FoodTech in the Master's in Technology and Sustainability of the Food IndustryWednesday, 24 January 2024 09:37
- Presentation of the ARIES4 Project to the Members of the NAVE2 AllianceThursday, 23 November 2023 06:43
- Bulgarian students in support of businessTuesday, 21 November 2023 10:01
From S3 to S4
Towards Sustainable Smart Specialisation Strategies
Smart specialization is now facing a major evolution with the proposal of moving from the current smart specialization strategy (S3) to smart specialisation strategies for sustainable and inclusive growth (S4+). As noted by a recent report published by the Joint Research Center of the European Commission “S4+ means reinforcing the S3 mission-oriented policy approach with non-neutrality, direction, and system approach to engage regions in European initiatives dealing with missions. S4+ implies a policy shift in the way regions may consider setting policy priorities to push technological innovation and their responses to regional societal challenges.” This new paradigm in the smart specialization strategy for regions connects these strategies and actors at regional and national level with EU-wide policies such as the European Green Deal and the new European industrial strategy for a sustainable recovery to the new green and digital economy, an also with the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. In this sense, it repositions smart specialisation in the new EU policy agenda to use the unprecedented EU investment for local jobs creation in the post-Covid recovery.
This revolutionary transition from S3 to the new S4+ requires the cooperation and alignment of all actors involved in smart specialization strategies: (1) education, and in particular higher education (HE) and vocational education and training (VET), (2) the public sector, and especially the entities involved in the design and development of smart specialisation, (3) the business sector, with special focus on the companies belonging to the prioritized sectors of each region, and (4) society in general.
Sustainability is a multifaceted concept that encompasses technological, cultural, environmental, social and economic aspects. Each agent of an economy experiences different challenges and demands different solutions when confronting it. Besides, place-based policies such as smart specialization can be very effective in fostering sustainability, due to the exploitation of competitive advantages also in this pursuit, but at the same time, they require great amounts of benchmarking and mutual learning. For all these reasons, knowledge co-creation and sharing is essential in the arrival of sustainable specialization strategies, both between the agents of local innovation ecosystems and between regions themselves. Alliances for innovation are excellent tools for such intra and between-regions cooperation, as they have been conceived to promote precisely those two kinds of interaction.

Key Actors of S3-to-S4 Transition
For a fruitful cooperation and a successful transition from S3 to S4+, all the key regional actors must develop the necessary skills, tools, and attitudes to navigate the new scenario. In particular:
- S3 strategists need guidelines in the design of policies and incentives for other actors in the regional ecosystem during the S4+ rollout, as well as measuring tools to monitor the evolution of sustainability in the region and within each sector.
- Managers of different organizations, particularly SMEs, need to understand what sustainability means, how it shapes their span of action and how they can take advantage of it to improve their competitiveness in increasingly competitive international markets.
- Students, as future agents of change, need to become aware of the relevance of smart specialization for regional development and European convergence, as well as the challenges and opportunities that the transition to sustainable economies brings. They also need to develop entrepreneurial attitudes to seize those challenges in the future.
- Society at large, and specifically regional societies, need to be informed about the concrete efforts that are made at a regional level towards more sustainable and competitive economies. Besides, it demands that findings and best practices are quickly disseminated throughout the rest of Europe.
Our Mission
To promote knowledge creation and exchange among S3 agents (HEIs, VET providers, business sector, public sector and society in general) of several European regions, in order to strengthen the evidence base for the design and implementation of regional smart specialisation strategies, and to provide tools for its monitoring.
To foster corporate social responsibility and the transition to more sustainable business models, by developing training material based on best practices, building analysis tools for companies, and identifying and providing the skills required by company managers to drive the transition.
To stimulate entrepreneurial attitudes, mind-sets, and skills among the participant actors of regional innovation ecosystems, with a particular emphasis on HE and VET students, and to address this entrepreneurship to the challenges of the sustainable transition.
To generate communication structures to foster interaction within regions and among them, quickly communicating the generated knowledge and projecting it towards the rest of European regions.